Ayurvedic management of Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.9.59Keywords:
Ayurvedic treatment, Diabetes mellitus, HbA1c, Hyperglycemia, VairayadiAbstract
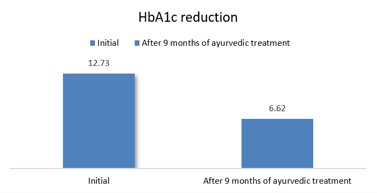
The type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with chronic hyperglycaemia and usually necessitates lifelong medication treatment; nevertheless, drawbacks like side effects of therapeutic agents, high costs of the drugs and non-compliance may subsequently shrink the clinical effectiveness. A case report details about a 33-year-old male diagnosed with uncontrolled T2DM, and who chose to stop the standard allopathic medicine and switch to purely Ayurvedic therapeutic approach. His baseline HbA1c was 12.73%, he had polydipsia, polyphagia, nocturia, fatigue, and erectile dysfunction. Ayurvedic protocol specific to the individual was followed, which included polyherbal preparations such as Vairayadi, Bhumi Amalaki Ghana, Chandraprabhavati, Lodhrasavam, etc., with dietary suggestions to focus on the low-glycaemic-index foods in addition to lifestyle interventions such as yoga and pranayama. At the end of the 9.5 months of treatment, the patient had reduced glycaemic burden significantly, and HbA1c had decreased to 6.62% (in absolute reduction 6.11%, in relative reduction 47.8%). At the same time, the fasting glucose was stabilized, nocturia and erectile dysfunction were resolved completely, no cases of hypoglycaemia or adverse effects were reported. Serum liver and renal function indicators were at normal level which proved the safety of the regime. These results endorse the plausibility of Ayurvedic herbal pharmacotherapy, dietary management, and orderly lifestyle alteration as an attentive and save standalone treatment measure in the management of the early phase, and moderately advanced T2DM. There is need to replicate and extend the preliminary observations in larger prospective studies.
Downloads
References
1. Accili D, Deng Z, Liu Q. Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2025 Jul;21(7):1–14. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-025-01114-y
2. Cade WT. Diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular diseases in the physical therapy setting. Phys Ther. 2008 Nov;88(11):1322–35. doi: https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20080008
3. Magliano DJ, Boyko EJ. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2022.
4. Little M, Humphries S, Patel K, Dewey C. Decoding the type 2 diabetes epidemic in rural India. Med Anthropol. 2017;36(2):96–110. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01459740.2016.1231676
5. Dhumal DC, Chavan VO, Keche A, Katole J. Exploring the Ayurvedic perspective on Prameha and its relevance to diabetes mellitus: a comparative analysis. J Ayurveda Integr Med Sci. 2024;13(7):102–10.
6. Sharma H, Chandola H. Prameha in Ayurveda: correlation with obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes mellitus. Part 1 – etiology, classification, and pathogenesis. J Altern Complement Med. 2011;17(6):491–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2010.0396
7. Murthy AV, Singh R. Concept of Prameha/Madhumeha (contradictions and compromises). Anc Sci Life. 1989;9(2):71–9.
8. Kumar A, Shukla S, Chandrakar R. Nidanpanchaka of Madhumeha Vyadhi – a review article. J Ayurveda Integr Med Sci. 2024;9(7):143–7.
9. Dhurve SA. A review on Ayurvedic Nidanatmak concept of Madhumeha Vyadhi. Int J Sci Res. 2022;11(3):1202–8. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.21275/SR22324161700
10. Dujunco MM, Gorriceta JH, Dampil OA, Mirasol R. INITIATE study: insulin versus oral hypoglycemic agent as initial therapy for newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus type 2 – a systematic review and meta-analysis. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2014;29(2):172–9.
11. Unger J. Current strategies for evaluating, monitoring, and treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 2008;121(6 Suppl):S3–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.021
12. Bytzer P, Talley N, Jones M, Horowitz M. Oral hypoglycaemic drugs and gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes mellitus. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15(1):137–42. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.2001.00896.x
13. Shrestha JTM, Shrestha H, Prajapati M, Karkee A, Maharjan A. Adverse effects of oral hypoglycemic agents and adherence to them among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Nepal. J Lumbini Med Coll. 2017;5(1):34–40. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.22502/jlmc.v5i1.126
14. Lohar T, Kulkarni M. Role of Pathya-Apathya in the management of Prameha (type-2 diabetes mellitus). J Ayurveda Integr Med Sci. 2024;9(10):75–80. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.21760/jaims.9.10.11
15. Reddy A. Prameha and role of Pathya: a review. J Ayurveda Integr Med Sci. 2021;6(3):126–31.
16. Verma A, Pandey P. Role of Pathya-Apathya and yogic procedures in the management of Madhumeha (diabetes mellitus). Int J Ayurvedic Med. 2018;10(6):131–6.
17. Siribaddana S, Medagama A, Wickramasinghe N, Siribaddana NM, Agampodi S, Fernando D, et al. The effect of Salacia reticulata extract biscuits on blood sugar control of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a two-period, two-sequence, crossover, randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Cureus. 2023;15(9). doi: https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.45921
18. Beidokhti MN, Andersen MV, Eid HM, Villavicencio MLS, Staerk D, Haddad PS, et al. Investigation of antidiabetic potential of Phyllanthus niruri L. using assays for α-glucosidase, muscle glucose transport, liver glucose production, and adipogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;493(1):869–74. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.09.080
19. Kanetkar P, Singhal R, Kamat M. Gymnema sylvestre: a memoir. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2007;41(2):77–81. doi: https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.2007010
20. Vijayan D, Sibi G. Pterocarpus marsupium for the treatment of diabetes and other disorders. J Comp Med Alt Healthc. 2019;9(1):555754.
21. Sharma AK, Bharti S, Kumar R, Krishnamurthy B, Bhatia J, Kumari S, et al. Syzygium cumini ameliorates insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction via modulation of PPARγ, dyslipidemia, oxidative stress, and TNF-α in type 2 diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;119(3):205–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.11184fp
22. Kandunuri KK, White K, Smith E. An overview on the efficacy of herbs used in Ayurvedic formulations for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Int J Herb Med. 2016;4(5):116–21.
23. Upadhyay RK. Antidiabetic potential of plant natural products: a review. Int J Green Pharm. 2016;10(3):96–113.
24. Porat S, Weinberg-Corem N, Tornovsky-Babaey S, Schyr-Ben-Haroush R, Hija A, Stolovich-Rain M, et al. Control of pancreatic β cell regeneration by glucose metabolism. Cell Metab. 2011;13(4):440–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.02.012
25. Stohs SJ, Ray S. Anti-diabetic and anti-hyperlipidemic effects and safety of Salacia reticulata and related species. Phytother Res. 2015;29(7):986–95. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5382
26. Sowjanya K, Girish C, Bammigatti C, Lakshmi NCP. Efficacy of Phyllanthus niruri on improving liver functions in patients with alcoholic hepatitis: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Indian J Pharmacol. 2021;53(6):448–56. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/ijp.IJP_540_20
27. Christa SS, Swetha A, Christina E, Ganesh RN, Viswanathan P. Modulatory effect of Chandraprabha Vati on antimicrobial peptides and inflammatory markers in kidneys of mice with urinary tract infection. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2013;7(5):390.
28. Butala MA, Kukkupuni SK, Vishnuprasad CN. Ayurvedic anti-diabetic formulation Lodhrasavam inhibits alpha-amylase, alpha-glucosidase and suppresses adipogenic activity in vitro. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2017;8(3):145–51. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaim.2017.03.005
29. Rajan P, Nair LP, Chandran H, Esanamangalam M. Exploring the health benefits and therapeutic uses of Amruthotharam Kashayam. Int J Ayurveda Pharma Res. 2025;13(4):68–70. doi: https://doi.org/10.47070/ijapr.v13i4.3626
30. Mahanta NR, Sahoo P. A clinical study on the effect of Lodhradi Kashaya on Madhumeha with special reference to diabetes mellitus (type-2). J Ayurveda Integr Med Sci. 2023;8(11):27–38.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Abhishek R. Patel, Pranav C. Patel

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














