Indigestion (Ajirna) - Induced Hyperacidity (Vishatabhdhajirna) Treated with Ayurveda Therapy : A Single Case Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.5.38Keywords:
Ajirna, Vishatabdhajirna, Agni dysfunction, Vata Dosha, Ayurvedic Shaman therapy, Hyperacidity, Reflux Disease Questionnaire (RDQ), Indigestion, Vata Vriddhi symptoms, Case reportAbstract
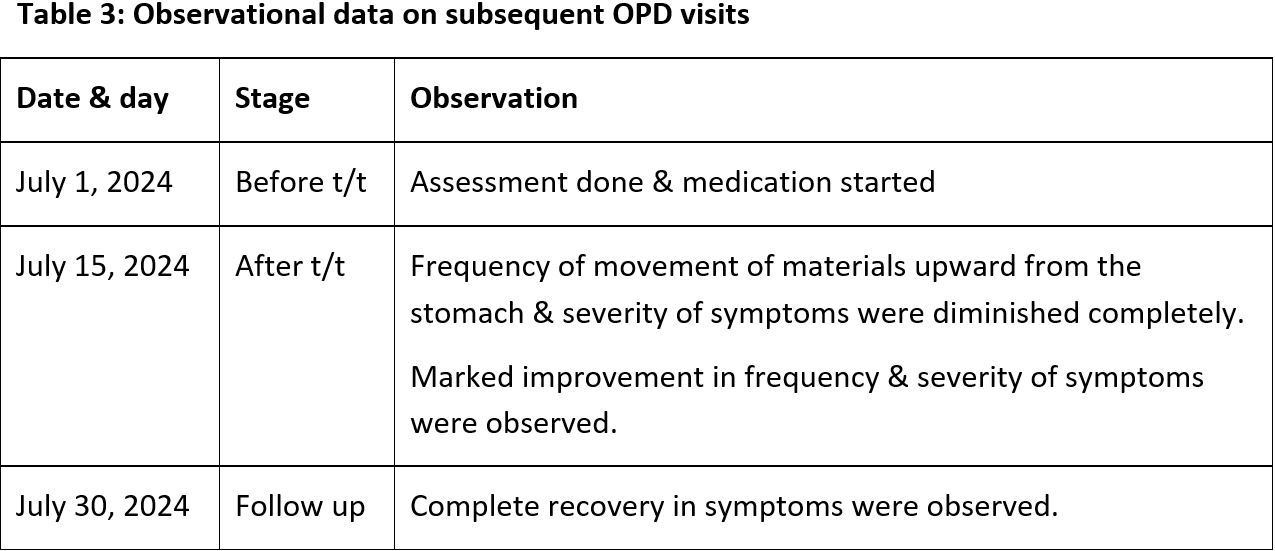
Ayurved the Indian traditional system of medicine, belives that the a majority of the diseases in humans arises due to hypofunctioning of Agni. Disturbed function of Agni causing indigestion of food is termed as Ajirna in Ayurveda. Vishatabhdhajirna are the types of Ajirna having vatadoshain its manifestation. Vishatabhdhajirnas can be compared with indigestion induced hyperacidity because of the resembelence in signs & symptoms observed in these conditions. In this report, we are presenting a case of 35 year old male patient diagnosed with Vishatabhajirna. With complaints of pricking pain in abdomen, abnormal movement of Vata, obstruction to stool and flatus and other symptoms of Vata Vridhhi. This case was treated with Ayurved Shaman therapy prescribed at a specific drug administration time along with cessation of known etiological factors. Therapeutic assessment was done by using Reflux Disease Questionnaire (RDQ) scale. Significant improvement was noted in clinical parameters as well as on the standard RDQ scale without reported relapse of previous symptoms on follow-up visit. Also, there were no adverse events recorded during the treatment & follow-up period.
Downloads
References
Tripathi B, editor. Madhav Nidan of Madhavkara. Ch. 6, Ver. 11, Agnimandya-Ajirna-Visuchika-Alasaka-Bilambika Nidan. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan; 2006. p. 230–1.
Shastri A, editor. Sushruta Samhita of Sushruta. Sutra Sthan, Ch. 46, Ver. 500–502; Uttar Tantra, Ch. 64, Ver. 69; Ch. 6, Ver. 74. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Surbharati Prakashan; 2003. p. 289, 813, 210.
Claret D, Hachem C. GERD. J Mo State Med Assoc. 2018;115:214–8.
Yibirin M, De Oliverira R, Plitt AE, Lutgen S. Adverse effects associated with PPI use. Cureus. 2021.
Shaw M. The reflux disease questionnaire: a measure for assessment of treatment response in clinical trials. Dent J. 2008.
Chuner KC, Pandey GS, editors. Bhavprakash Nighantu of Shri Bhavmishra. Ver. 1–5, 18–24, 32, 109–13. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Bharati Academy; 2010.