A Review on Pathya-Apathya in Amlapitta: Key to Holistic Healing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.9.11Keywords:
Amlapitta, Pathya, Apathya, Pitta, AgniAbstract
Amlapitta (Hyperacidity or Acid dyspepsia), a prevalent gastrointestinal condition described in Ayurvedic literature, presents with symptoms such as acid regurgitation, nausea, burning sensation, and indigestion, closely resembling hyperacidity in modern medicine. Its pathogenesis primarily involves the vitiation of Pitta Dosha and impaired Agni, often triggered by improper dietary and lifestyle practices. The Ayurvedic principle of Pathya-Apathya - wholesome and unwholesome food and behaviour - forms a cornerstone in the prevention and management of Amlapitta. This review explores the classical and contemporary understanding of dietary and lifestyle recommendations in Amlapitta, emphasizing their role in disease prevention, palliation, and recurrence control. Pathya includes the intake of cooling, light, non-spicy, and easily digestible foods, along with regular meals, adequate rest, and stress reduction. In contrast, Apathya consists of spicy, sour, fermented, and oily foods, erratic eating habits, and excessive mental stress, all of which aggravate Pitta and weaken digestive function. Ayurvedic texts advocate individualized dietary regimens based on factors such as Prakriti (constitution), Agni (digestive capacity), Ritu (season), and Roga-Avastha (disease stage). Integrating this personalized Pathya-Apathya framework can significantly enhance the efficacy of therapeutic interventions. This paper highlights the preventive, promotive, and therapeutic relevance of dietary discipline in managing Amlapitta, supported by textual references and recent clinical observations.
Downloads
References
Maheshwari BMSV, Negalur VB. Role of Pathya and Apathya in Amlapitta. Int J Ayurveda Pharm Chem. 2024 Jul 10;21.
Sastri H. Amarakosha. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan; 2000. p. 408.
Tripathi B, editor. Charak Samhita of Agnivesa: Chikitsasthana – Dirghajivitiya Adhyaya, Adhyaya 1, Sutra 60. 1st ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Surbharati Prakashan; 2021. p. 27.
Shastri A, editor. Sushrut Samhita of Maharshi Sushrut: Sutrasthana – Vranaprashna Adhyaya, Adhyaya 21, Sutra 11. 1st ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan; 2017. p. 116.
Tripathi B, editor. Charak Samhita of Agnivesa: Chikitsasthana – Grahanidoshachikitsa Adhyaya, Adhyaya 15, Sutra 42–44. 1st ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Surbharati Prakashan; 2021. p. 467.
Tripathi B, editor. Madhava Nidanam of Shri Madhavkara: Amlapitta Nidan Adhyaya, Adhyaya 51, Sutra 2. 1st ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Surbharati Prakashan; 2019. p. 226.
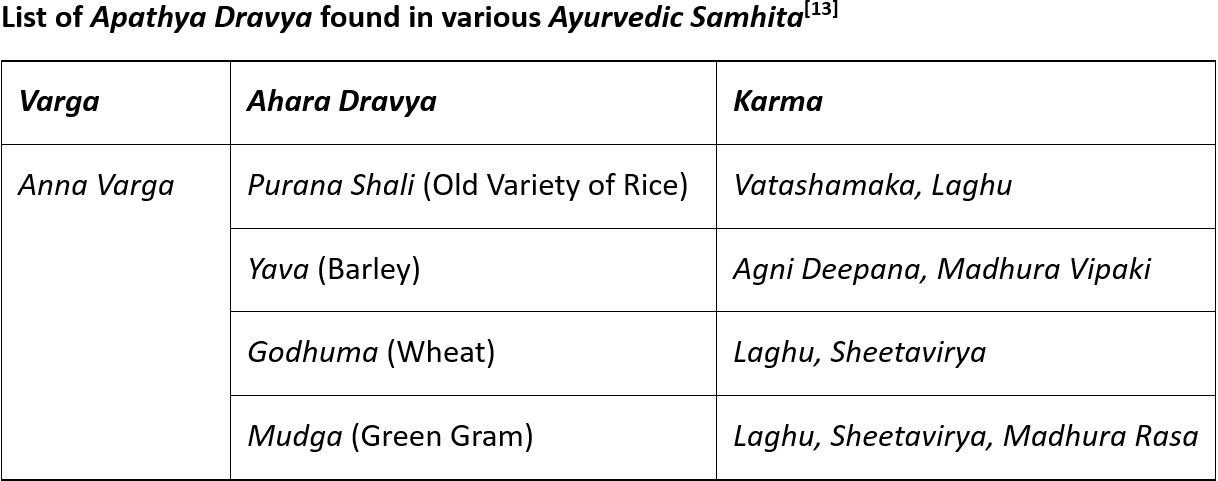
Tripathi B, editor. Madhava Nidanam of Shri Madhavkara: Amlapitta Nidan Adhyaya, Adhyaya 51, Sutra 2. 1st ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Surbharati Prakashan; 2019. p. 226.
Bhavamishra. Bhavaprakasha, Part 2. Edited with Hindi commentary by Mista BS. 11th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Bhavan; 2007. Madhyamakhanda 10/13.
Jivaka V. Kashyapa Samhita. With Sanskrit introduction by Sharma H. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan; 2006. Khilasthana 16/38–40.
Bhavamishra. Bhavaprakasha, Part 2. Edited with Hindi commentary by Mista BS. 11th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Bhavan; 2007. Madhyamakhanda 10/14.
Govindadasa. Bhaishajya Ratnavali. Vidyotini Hindi Teeka by Shastri AD. 24th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan; 2004. p. 29/95–96.
Bhavamishra. Bhavaprakasha, Part 2. Edited with Hindi commentary by Mista BS. 11th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Bhavan; 2007. Madhyamakhanda 10/14.
Ahire VR, Dachewar AS. A review on Pathya Apathya in the management of Amlapitta Vyadhi. Ayurline Int J Res Indian Med. 2021 Apr–Jun;5(2).
Ahire VR, Dachewar AS. A review on Pathya Apathya in the management of Amlapitta Vyadhi. Ayurline Int J Res Indian Med. 2021 Apr–Jun;5(2).
Mali RS, Borakhade VR. Pathya and Apathya in Amlapitta. AyurDarpana J Indian Med. 2019 Apr–Jun;4(2).
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Amrutha Jayan, Jai Singh Yadav, Sneha John

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.














