Shodhana and Shamana Chikitsa in Autoimmune Disorders: An Ayurvedic Perspective
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.6.43Keywords:
Autoimmune Disorders, Shodhana Chikitsa, Shamana Chikitsa, Ama, Agni Dushti, Immunomodulation, Tridosha, RasayanaAbstract
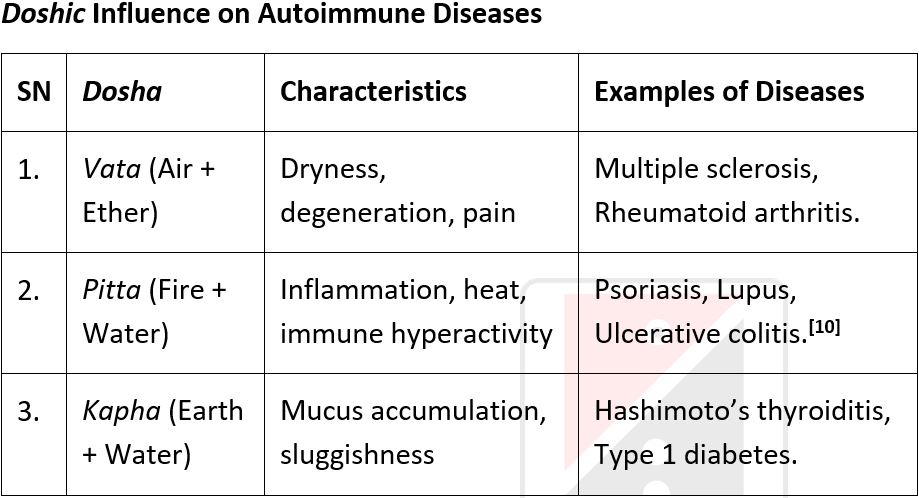
Autoimmune disorders represent a group of complex, chronic diseases characterized by aberrant immune responses where in the body's immune system attacks its own tissues. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease are increasingly prevalent, and their etiology often remains unclear in conventional medicine. From an Ayurvedic perspective, these disorders can be understood through the lens of Agni Dushti, Ama formation, and Tridosha imbalance, leading to Srotorodha (obstruction of bodily channels) and Dhatukshaya (tissue depletion). Ayurveda offers a comprehensive approach to such conditions through two primary therapeutic modalities: Shodhana Chikitsa (purificatory therapy) and Shamana Chikitsa (palliative therapy). Shodhana aims to eliminate the accumulated Doshas and Ama from the body, thereby addressing the root cause of disease. Therapies like Virechana, Basti, and Raktamokshana have shown promise in managing various autoimmune pathologies. Conversely, Shamana Chikitsa involves internal medications, dietary regulation, and lifestyle modifications to balance the Doshas and strengthen the immune system. Herbs such as Guduchi, Ashwagandha, Haridra, and formulations like Kaishora Guggulu and Amritarishta are known for their immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties. This article aims to present a holistic Ayurvedic framework for understanding and managing autoimmune disorders, focusing on both Shodhana and Shamana principles. Integrating classical knowledge with modern clinical insights, it highlights the potential of Ayurveda to offer safe, effective, and individualized care in autoimmune disease management, emphasizing the importance of detoxification, immune modulation, and restoration of homeostasis.
Downloads
References
Davidson A, Diamond B. Autoimmune diseases. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(1):54–66. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra34324
Graham KL, Utz PJ, Anderson MS. Antigen-specific tolerance in autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018;36:25–50. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053343
Tripathi B. Charaka Samhita with Hindi Commentary. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Surbharati; 2018.
Mishra A, Singh BB, Dagenais S, Nampoothiri V. Ayurveda in the management of chronic diseases. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2020;11(4):405–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaim.2020.03.003
Sharma P, Joshi K, Rastogi S. Ayurvedic concepts of Ama and Agni in immune-related disorders. Ayurveda Res Ther. 2021;13(2):65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.art.2022.02.008
Tripathi S, Gupta R, Verma P. Ayurvedic classification of Ama Vata and its clinical significance. Int J Ayurveda Stud. 2019;8(1):40–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijas.2019.01.003
Desai P, Patwardhan B. The role of Ojas in immunological diseases: A critical analysis. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2020;12(2):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaim.2021.01.011
Rastogi S. Understanding autoimmune disorders through Ayurveda: Agni, Ama, and inflammation. Indian J Ayurveda Res. 2022;13(1):45–60.
Bhardwaj R, Kumar A. Ayurvedic intervention in autoimmune disorders: A review. Int J Ayurveda Res. 2020;11(3):120–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2020.03.002
Mishra A, Kumar P. Pitta imbalance and inflammatory diseases in Ayurveda. Varanasi: Varanasi Ayurveda Publishers; 2020.
Patgiri BJ, Prajapati PK, Shukla VJ. Role of Panchakarma in the management of autoimmune diseases: A review. Ayu. 2012;33(3):365–70.
Chaudhary A, Singh N. Role of Panchakarma in autoimmune disorders. Ayu. 2010;31(4):475–8.
Gogte VM. Ayurvedic Pharmacology and Therapeutic Uses of Medicinal Plants. Mumbai: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan; 2000.
Dwivedi V, Sharma S. Clinical importance of Rasayana therapy in chronic diseases. Int J Ayurveda Pharma Res. 2014;2(4):23–8.
Panda B. Principles of Ayurveda. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Publications; 2006.
Kumar A. Ayurvedic dietetics: Relevance in lifestyle diseases. Ayu. 2012;33(3):367–72.
Singh RH, Nariya M, Galib R. Ayurvedic lifestyle and its impact on autoimmune conditions: A clinical perspective. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2015;6(3):213–9.
Tolahunase M, Sagar R, Dada R, Sharma R. Impact of Yoga and Meditation on cellular aging in stressed individuals: A prospective randomized controlled study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:7928981.
Mukherjee PK, Wahile A. Integrated approaches towards drug development from Ayurveda and other Indian system of medicines. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;103(1):25–35.
Sharma R, Amin H, Galib R. Challenges in standardization of Ayurvedic formulations: A review. Ayu. 2010;31(4):408–12.
Sahoo N, Manchikanti P, Dey S. Herbal drugs: Standards and regulation. Fitoterapia. 2011;82(1):44–55.
Gogtay NJ, Bhatt HA, Dalvi SS, Kshirsagar NA. The use and safety of non-allopathic Indian medicines. Drug Saf. 2002;25(14):1005–19.