Insight to effect of Deepana Panchana Herbs on Gut microbiota
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21760/jaims.10.3.28Keywords:
Deepana, Pachana, Gut microbiota, AyurvedaAbstract
Introduction: Ayurveda has emphasized on being healthy by not only what we eat but also how we digest it. So utmost significance is given to Agni. The ancient science signifies the root cause of all metabolic disorder is imbalance of Agni told in terms of “Sarve Roga Api Mandagni”. Deepana Pachana (Appetizers and digestants) herbs are playing crucial role in treating any metabolic disease. The Gut Microbiota is collection of good bacteria, fungi, archaea and is key to many aspects to maintain Human health, builds up immunity, regulates metabolism and control neurobehavioral traits. The alteration in this Gut flora can lead to various metabolic disorders from Obesity to Cancer. Restoring the same with diet, probiotics, prebiotics and medicine is crucial for prevention and treatment for all these metabolic disorders. This review of Paper aims to identify the effect of Deepana, Pachana herbs on Gut microbiota.
Materials and Methods: Literature search was done in classical text of Ayurveda for Deepana and Pachana herbs. Relevant Database for gut microbiota and relevant research articles on herbs on gut microbiota were chosen and reviewed.
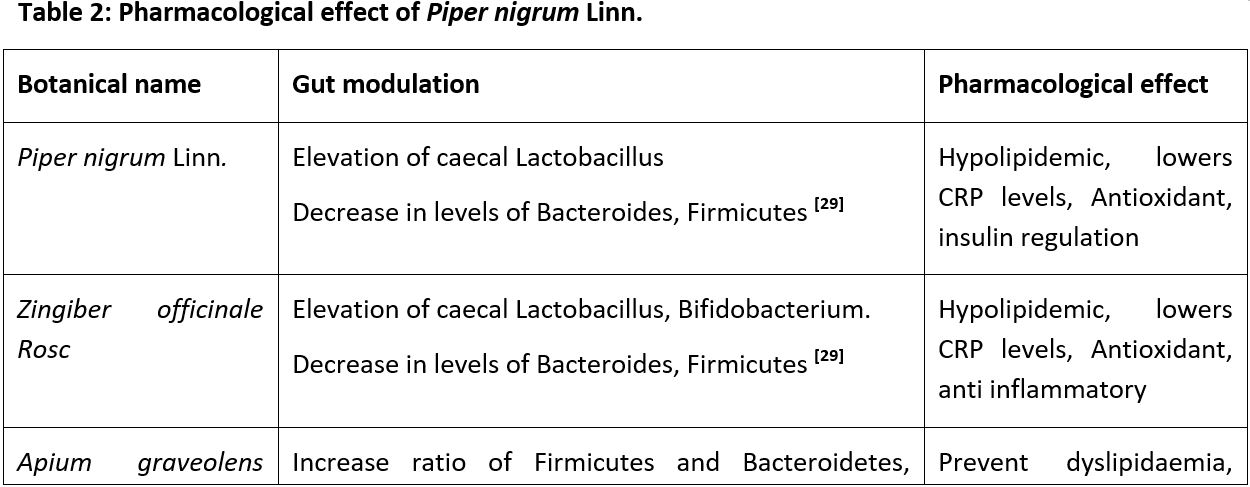
Result and Discussion: The review clarified that most of herbs that have Deepan, Pachana property have got Gut modulation effect and most of herbs have shown prebiotic potential gaining improvement in a positive gut bacterial alteration.
Conclusion: This gut modulation effect of herbs can be used to prevent obesity, Diabetes, Cardiovascular diseases, maximizing our Health and Immunity.
Downloads
References
Vachaspathyam. Available from: https://archive.org/details/VacaspatyamVolume/page/n49/mode/2up?q=agni.
Susrutha. Susrutha Samhita. Edited by Jadavji Trikamji, Narayana Ram Acarya. Sutrasthanam. Chaukhambha Orientala Jai Krishnadas Ayurveda Series No:34; Ch.1, Ver.7, Dalhana commentary. p.2.
Vagbhata. Ashtanga Hridayam. Revised and collated by Annamoreswar Kunte. Nidanasthana. Ch.12, Ver.1. Chaukambha Sanskrit Krishnadas Academy, Varanasi; Series 54, 2007. p.513.
Vagbhata. Ashtanga Hridayam. Revised and collated by Annamoreswar Kunte. Sutrasthana. Ch.14, Ver.6. Chaukambha Sanskrit Krishnadas Academy, Varanasi; Series 54, 2007. p.223.
Vagbhata. Ashtanga Hridayam. Revised and collated by Annamoreswar Kunte. Sutrasthana. Ch.14, Ver.12. Chaukambha Sanskrit Krishnadas Academy, Varanasi; Series 4, 2007. p.225.
Vagbhata. Ashtanga Hridayam. Revised and collated by Annamoreswar Kunte. Sutrasthana. Ch.13, Ver.29. Chaukambha Sanskrit Krishnadas Academy, Varanasi; Series 4, 2007. p.217.
Valdes AM, Walter J, Segal E, Spector TD. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ 2018;361:k2179. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k2179.
Zhang H, Sparks JB, Karyala SV, Settlage R, Luo XM. Host adaptive immunity alters gut microbiota. ISME J 2015;9:770-81. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2014.165.
Wiley NC, Dinan TG, Ross RP, Stanton C, Clarke G, Cryan JF. The microbiota-gut-brain axis as a key regulator of neural function and the stress response: Implications for human and animal health. J Anim Sci 2017;95:3225-46. pmid:28727115.
Peterson CT, Denniston K, Chopra D. Therapeutic uses of Triphala in Ayurvedic medicine. J Altern Complement Med 2017;23(8):607–14. doi: 10.1089/acm.2017.0083.
Manichanh C, Rigottier-Gois L, Bonnaud E, et al. Reduced diversity of faecal microbiota in Crohn’s disease revealed by a metagenomic approach. Gut 2006;55:205-11. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.073817.
Scher JU, Ubeda C, Artacho A, et al. Decreased bacterial diversity characterizes the altered gut microbiota in patients with psoriatic arthritis, resembling dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015;67:128-39. doi: 10.1002/art.38892.
de Goffau MC, Luopajärvi K, Knip M, et al. Fecal microbiota composition differs between children with β-cell autoimmunity and those without. Diabetes 2013;62:1238-44. doi: 10.2337/db12-0526.
Lambeth SM, Carson T, Lowe J, et al. Composition, diversity and abundance of gut microbiome in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Obes 2015;2:1-7. pmid:26756039.
Menni C, Lin C, Cecelja M, Mangino M, Matey-Hernandez ML, Keehn L, Mohney RP. Gut microbial diversity is associated with lower arterial stiffness in women. Eur Heart J 2018. Available from: https://academic.oup.com.
Sharangadhara. Sharangadhara Samhita. Collated by Pandit Parasuramasastri Vidyasagar. Chaukambha Sanskrit Krishnadas Academy, Varanasi; Series 14, Purvakhanda 4/1. p.33.
Vagbhata. Ashtanga Hridayam. Revised and collated by Annamoreswar Kunte. Sutrasthana. Ch.14, Ver.12. Chaukambha Sanskrit Krishnadas Academy, Varanasi; Series 4, 2007. p.225.
Vagbhata. Ashtanga Hridayam. Revised and collated by Annamoreswar Kunte. Sutrasthana. Ch.13, Ver.29. Chaukambha Sanskrit Krishnadas Academy, Varanasi; Series 4, 2007. p.217.
Shastri Kashinath, Pandey Gangasahaya. Charak Samhita (Hindi commentary). Vol.I (Sutra sthana Ch.4/9). Varanasi: Chaukhamba Sanskrit Sansthan; 2004. p.60.
Sastry JLN. Dravyaguna Vijnan. Reprint edition. Varanasi: Chaukhamba Orientalia; 2015. p.452, p.561, p.574, p.31, p.871, p.656, p.448, p.266, p.135, p.254.
Wadikar DD, Patki PE, Sharma RK. Appetizer: A food category or food adjective? Indian J Nutri. 2018;5(1):185. Available from: https://www.opensciencepublications.com/fulltextarticles/IJN-2395-2326-5-185.html.
Haque E, Roy CA, Rani M. Review on phytochemical and pharmacological investigation of Piper chaba Hunter. Int J Sci Eng Res. 2018;9(3):937-941. [Cited 2021 Apr 27].
Roy A, Bharadvaja N. A review on pharmaceutically important medicinal plant: Plumbago zeylanica. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331968339. [Cited 2021 Apr 27].
Pertz HH, Lehmann J, Roth-Ehrang R, Elz S. Effects of ginger constituents on the gastrointestinal tract: Role of cholinergic M3 and serotonergic 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptors. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/49821359. [Cited 2021 Apr 27].
Paul S, Ali MY, Rumpa NE, et al. Assessment of toxicity and beneficiary effects of Garcinia pedunculata on hematological, biochemical, and histological homeostasis in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:4686104. doi: 10.1155/2017/4686104. [Cited 2021 Apr 27].
Takooree H, Aumeeruddy MZ, Rengasamy KRR, et al. A systematic review on black pepper (Piper nigrum L.): From folk uses to pharmacological applications. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(Suppl 1):S210-S243. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1565489. [Cited 2021 Apr 29].
Al-Asmari AK, Athar MT, Kadasah SG. An updated phytopharmacological review on medicinal plant of Arab region: Apium graveolens Linn. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5414449/. doi: 10.4103/phrev.phrev_35_16. [Cited 2021 Apr 27].
Balachandran P. Semecarpus anacardium Linn. nuts—A boon in alternative medicine. Indian J Exp Biol. 2001;38(12):1177-82.
Kondapalli NB, Hemalatha R, Uppala S, et al. Effects of Ocimum sanctum, Zingiber officinale, and Piper nigrum extracts on gut microbiota modulations (prebiotic potential), basal inflammatory markers and lipid levels: Oral supplementation study in healthy rats. Pharm Biol. 2022;60(1):437-450. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2033797.
Zhao D, Cao J, Jin H, et al. Beneficial impacts of fermented celery (Apium graveolens L.) juice on obesity prevention and gut microbiota modulation in high-fat diet fed mice. Food Funct. 2021;12(19):9151-9164. doi: 10.1039/d1fo00560j.
Pendse GS, Iyenger MA. Plumbago zeylanica L. (Chitrak): A gastrointestinal flora normalizer. Planta Med. 1966;14(3):337-351. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1100060.
O’Flaherty S, Cobian N, Barrangou R. Impact of pomegranate on probiotic growth, viability, transcriptome, and metabolism. Microorganisms. 2023;11(2):404. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020404.
Alves-Santos AM, Sugizaki CSA, Lima GC, Naves MMV. Prebiotic effect of dietary polyphenols: A systematic review. J Funct Foods. 2020;74:104169. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104169.
Zhu J, He L. The modulatory effects of curcumin on the gut microbiota: A potential strategy for disease treatment and health promotion. Microorganisms. 2024;12(4):642. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040642.
Alhomsi A, Bayraktar MK. Effects of several culinary herbs and spices on gut microbiota. Food Health. 2024;10(4):296-305.